House insurance coverage charges are emerging in the USA, no longer most effective in Florida, which noticed tens of billions of bucks in losses from hurricanes Helene and Milton, however around the nation.
In line with S&P World Marketplace Intelligence, householders insurance coverage higher a mean of eleven.3% national in 2023, with some states, together with Texas, Arizona and Utah, seeing just about double that build up. Some analysts expect a mean build up of about 6% in 2024.
Those will increase are pushed through a potent mixture of emerging insurance coverage payouts coupled with emerging prices of building as other people construct an increasing number of pricey houses and different belongings in hurtŌĆÖs means.
When house insurance coverage averages $2,377 a yr nationally, and $11,000 consistent with yr in Florida, this can be a blow to many of us. In spite of those emerging charges, Jacques de Vaucleroy, chairman of the board of reinsurance large Swiss Re, believes U.S. insurance coverage continues to be priced too low to totally duvet the hazards.
It isnŌĆÖt simply that premiums are converting. Insurers now regularly scale back protection limits, cap payouts, build up deductibles and impose new stipulations and even exclusions on some commonplace perils, corresponding to coverage for wind, hail or water harm. Some require sure preventive measures or observe risk-based pricing ŌĆō charging extra for houses in flood plains, wildfire-prone zones, or coastal spaces prone to hurricanes.
Householders observing their costs upward push quicker than inflation may suppose one thing sinister is at play. Insurance coverage firms are dealing with impulsively evolving dangers, then again, and looking to value their insurance policies low sufficient to stay aggressive however prime sufficient to hide long run payouts and stay solvent in a stormier local weather. This isnŌĆÖt a very simple activity. In 2021 and 2022, seven belongings insurers filed for chapter in Florida on my own. In 2023, insurers misplaced cash on householders protection in 18 states.
However those adjustments are elevating alarm bells. Some trade insiders fear that insurance coverage is also shedding its relevance and price ŌĆō actual or perceived ŌĆō for policyholders as protection shrinks, premiums upward push and exclusions build up.
How insurers assess threat
Insurance coverage firms use advanced fashions to estimate the possibility of present dangers in keeping with previous occasions. They mixture ancient information ŌĆō corresponding to tournament frequency, scale, losses and contributing elements ŌĆō to calculate value and protection.
Then again, the rise in screw ups makes the previous an unreliable measure. What used to be as soon as regarded as a 100-year tournament would possibly now be higher understood as a 30- or 50-year tournament in some places.
What many of us donŌĆÖt understand is that the upward thrust of so-called ŌĆ£secondary perilsŌĆØ ŌĆō an insurance coverage trade time period for floods, hailstorms, sturdy winds, lightning moves, tornadoes and wildfires that generate small to mid-size harm ŌĆō is changing into the principle driving force of the insurability problem, in particular as those occasions develop into extra intense, common and cumulative, eroding insurersŌĆÖ profitability over the years.
A twister tore the roof off a house in Madison, Tenn., in 2023. The 2024 twister season used to be some of the busiest on file.
Jon Cherry/Getty Pictures
Local weather exchange performs a job in those emerging dangers. Because the local weather warms, air can hang extra moisture ŌĆō about 7% extra with each and every level Celsius of warming. That results in more potent downpours, extra thunderstorms, better hail occasions and the next threat of flooding in some areas. The U.S. used to be on reasonable 1.5 levels Celsius (2.6 levels Fahrenheit) hotter in 2022 than in 1970.
Insurance coverage firms are revising their fashions to stay alongside of those adjustments, a lot as they did when smoking-related sicknesses was an important value burden in existence and medical health insurance. Some firms use local weather modeling to reinforce their same old actuarial threat modeling. However some states were hesitant to permit local weather modeling, which will depart firms systematically underrepresenting the hazards they face.
Every corporate develops its personal evaluation and geographic technique to succeed in a distinct conclusion. For instance, Innovative Insurance coverage has raised its home-owner charges through 55% between 2018 and 2023, whilst State Farm has raised them most effective 13.7%.
Whilst a house owner who chooses to make house enhancements, corresponding to putting in a luxurious kitchen, can be expecting an build up in premiums to account for the added substitute worth, this impact is most often small and predictable. In most cases, the extra really extensive top class hikes are because of the ever-increasing threat of critical climate and herbal screw ups.
Insurance coverage for insurers
When dangers develop into too unpredictable or unstable, insurers can flip to reinsurance for assist.
Reinsurance firms are necessarily insurance coverage firms that insure insurance coverage firms. However lately, reinsurers have identified that their threat fashions also are now not correct and feature raised their charges accordingly. Assets reinsurance on my own higher through 35% in 2023.
Reinsurance may be no longer rather well suited for protecting secondary perils. The standard reinsurance type is excited by massive, uncommon catastrophes, corresponding to devastating hurricanes and earthquakes.
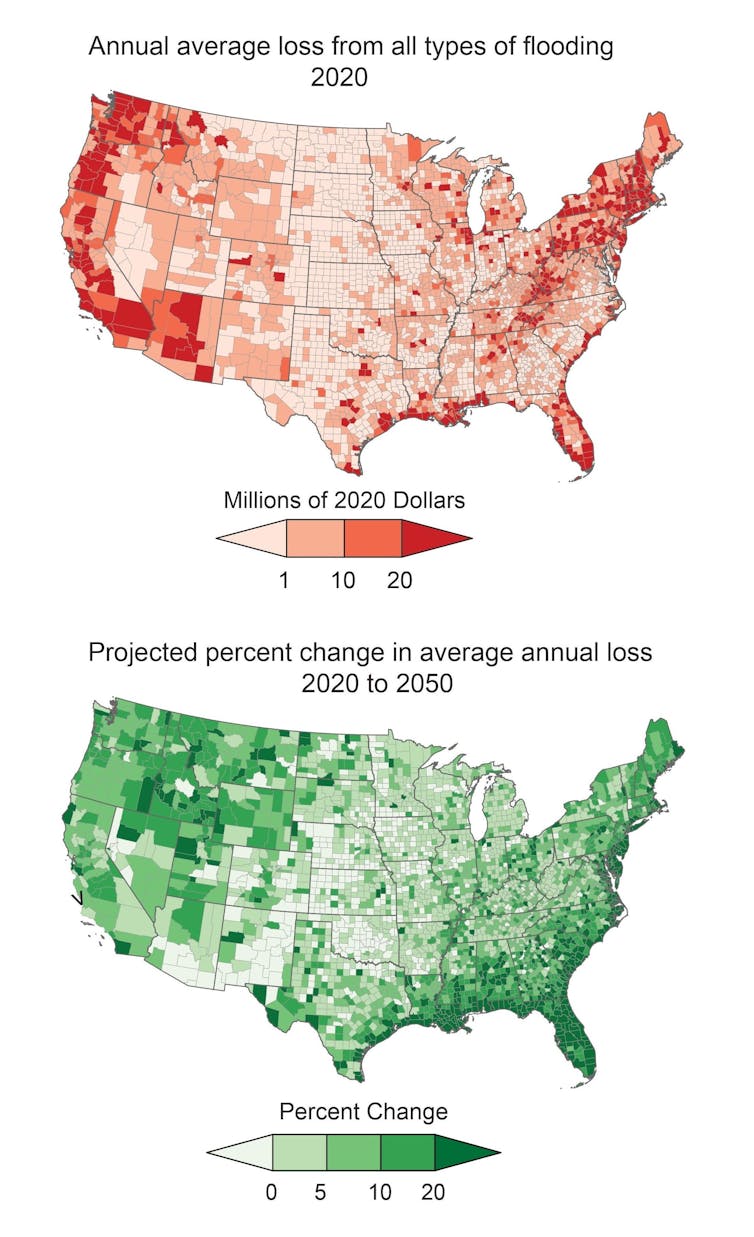
Maps illustrate the common loss from flooding on my own and anticipated will increase through mid-century. About 90% of catastrophes within the U.S. contain flooding, however simply 6% of U.S. householders have flood insurance coverage.
5th Nationwide Local weather Evaluate
As a substitute, some insurers are shifting towards parametric insurance coverage, which gives a predefined fee if an tournament meets or exceeds a predefined depth threshold. Those insurance policies are more economical for customers for the reason that payouts are capped and canopy occasions corresponding to a magnitude 7 earthquake, over the top rain inside a 24-hour duration or a Class 3 storm in an outlined geographical house. The boundaries permit insurers to offer a more economical type of insurance coverage this is much less prone to critically disrupt their price range.
Protective the patron
After all, insurers donŌĆÖt function in a wholly loose marketplace. State insurance coverage regulators evaluation insurance coverage firmsŌĆÖ proposals to boost charges and both approve or deny them.
The insurance coverage trade in North Carolina, for instance, the place Storm Helene brought about catastrophic harm, is arguing for a house owner top class build up of greater than 42% on reasonable, starting from 4% in portions of the mountains to 99% in some waterfront spaces.
If a fee build up is denied, it would pressure an insurer to easily withdraw from sure marketplace sectors, cancel current insurance policies or refuse to write down new ones when their ŌĆ£loss ratioŌĆØ ŌĆō the ratio of claims paid to premiums amassed ŌĆō turns into too prime for too lengthy.
Since 2022, seven of the highest 12 insurance coverage carriers have both lower current householders insurance policies or stopped promoting new ones within the wildfire-prone California home-owner marketplace, and an equivalent quantity have pulled again from the Florida marketplace because of the growing value of hurricanes.
To stem this tide, California is reforming its rules to hurry up the speed build up approval procedure and make allowance insurers to make their case the use of local weather fashions to pass judgement on wildfire threat extra as it should be.
Florida has instituted regulatory reforms that experience lowered litigation and related prices and has got rid of 400,000 insurance policies from the state-run insurance coverage program. Consequently, 8 insurance coverage carriers have entered the marketplace there since 2022.
Having a look forward
Answers to the mounting insurance coverage disaster additionally contain how and the place other people construct. Construction codes can require extra resilient houses, corresponding to how hearth protection requirements higher the effectiveness of insurance coverage many many years in the past.
By means of one estimate, making an investment $3.5 billion in making the two-thirds of U.S. houses no longer lately as much as code extra resilient to storms may save insurers up to $37 billion through 2030.
After all, if affordability and relevance of insurance coverage proceed to degrade, actual property costs will begin to decline in uncovered places. This would be the maximum tangible signal that local weather exchange is using an insurability disaster that disrupts wider monetary balance.
Justin DŌĆÖAtri, Local weather Trainer on the training platform Adaptify U and Sustainability Transformation Lead at Zurich Insurance coverage Team, contributed to this text.













