Within the twentieth century, when a regimen an infection used to be handled with an ordinary antibiotic, restoration used to be anticipated. However through the years, the microbes answerable for those infections have advanced to evade the very medication designed to get rid of them.
Each and every 12 months, there are greater than 2.8 million antibiotic-resistant infections in the US, resulting in over 35,000 deaths and US$4.6 billion in well being care prices. As antibiotics transform much less efficient, antimicrobial resistance poses an expanding danger to public well being.
Antimicrobial resistance started to emerge as a significant danger within the Forties with the upward push of penicillin resistance. By means of the Nineteen Nineties, it had escalated into a world fear. A long time later, vital questions nonetheless stay: How does antimicrobial resistance emerge, and the way can scientists observe the hidden adjustments resulting in it? Why does resistance in some microbes stay undetected till a scourge happens? Filling those wisdom gaps is a very powerful to combating long run outbreaks, bettering remedy results and saving lives.
Antimicrobial resistance will also be fatal.
Over time, my paintings as a microbiologist and biomedical scientist has concerned with investigating the genetics of infectious microbes. My colleagues and I known a resistance gene up to now undetected within the U.S. the usage of genetic and computational strategies that may assist reinforce how scientists stumble on and observe antimicrobial resistance.
Demanding situations of detecting resistance
Antimicrobial resistance is a herbal procedure the place microbes continuously evolve as a protection mechanism, obtaining genetic adjustments that reinforce their survival.
Sadly, human actions can accelerate this procedure. The overuse and misuse of antibiotics in well being care, farming and the surroundings push micro organism to genetically exchange in ways in which let them continue to exist the medication intended to kill them.
Early detection of antimicrobial resistance is a very powerful for efficient remedy. Surveillance in most cases starts with a laboratory pattern received from sufferers with suspected infections, which is then analyzed to spot doable antimicrobial resistance. Historically, this has been accomplished the usage of culture-based strategies that contain exposing microbes to antibiotics within the lab and staring at whether or not they survived to decide whether or not they have been changing into resistant. In conjunction with serving to government and researchers observe the unfold of antimicrobial resistance, hospitals use this strategy to make a decision on remedy plans.
On the other hand, culture-based approaches have some barriers. Resistant infections frequently move disregarded till antibiotics fail, making each detection and intervention processes gradual. Moreover, new resistance genes would possibly get away detection altogether.
Genomics of antimicrobial resistance
To triumph over those demanding situations, researchers have built-in genomic sequencing into antimicrobial resistance surveillance. Thru whole-genome sequencing, we will be able to analyze the entire DNA in a microbial pattern to get a complete view of the entire genes provide ‚Äď together with the ones answerable for resistance. With the computational gear of bioinformatics, researchers can successfully procedure huge quantities of genetic knowledge to reinforce the detection of resistance threats.
Regardless of its benefits, integrating genomic sequencing into antimicrobial resistance tracking gifts some demanding situations of its personal. Prime prices, high quality assurance and a scarcity of educated bioinformaticians make implementation tough. Moreover, the complexity of decoding genomic knowledge would possibly restrict its use in medical and public well being decision-making.
Bioinformatics lets in researchers to research massive organic datasets.
hh5800/iStock by way of Getty Photographs Plus
Organising world requirements may just help in making whole-genome sequencing and bioinformatics an absolutely dependable software for resistance surveillance. The Global Well being Group recommends laboratories practice strict high quality keep an eye on measures to make sure correct and related effects. This contains the usage of dependable, user-friendly computational gear and shared microbial databases. Further methods come with making an investment in coaching techniques and fostering collaborations between hospitals, analysis labs and universities.
Finding a resistance gene
Combining complete genome sequencing and bioinformatics, my colleagues and I analyzed Salmonella samples accumulated from a number of animal species between 1982 and 1999. We found out a Salmonella resistance gene referred to as blaSCO-1 that has refrained from detection in U.S. farm animals for many years.
The blaSCO-1 gene confers resistance to microbes in opposition to a number of vital antibiotics, together with ampicillin, amoxicillin-clavulanic acid and, to a point, cephalosporins and carbapenems. Those medicines are a very powerful for treating infections in each people and animals.
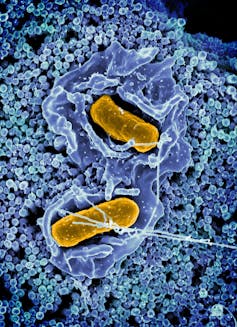
Salmonella Typhimurium invading a cellular.
NIAID/Flickr, CC BY-SA
The blaSCO-1 gene most likely remained unreported as a result of regimen surveillance generally goals well known resistance genes and it has overlapping purposes with different genes. Gaps in bioinformatics experience could have additionally hindered its identity.
The failure to stumble on genes like blaSCO-1 raises fear about its doable position in previous remedy screw ups. Between 2015 and 2018, the Facilities for Illness Keep an eye on and Prevention started enforcing whole-genome sequencing for regimen surveillance of Salmonella. Research performed all the way through this era discovered that 77% of multistate outbreaks have been connected to farm animals harboring resistant Salmonella.
Those neglected genes have important implications for each meals protection and public well being. Undetected antimicrobial resistance genes can unfold thru meals animals, infected meals merchandise, processing environments and agricultural runoff, permitting resistant micro organism to persist and achieve people. Those resistant micro organism result in infections which might be tougher to regard and build up the danger of outbreaks. Additionally, the worldwide motion of other folks, farm animals and items signifies that those resistant traces can simply pass borders, turning native outbreaks into international well being threats.
Figuring out new resistance genes no longer most effective fills a vital wisdom hole, but it surely additionally demonstrates how genomic and computational approaches can assist stumble on hidden resistance mechanisms ahead of they pose standard threats.
Strengthening surveillance
As antimicrobial resistance continues to upward push, adopting a One Well being method that integrates human, animal and environmental elements can assist make sure that rising resistance does no longer outpace people’ skill to battle it.
Projects just like the Quadripartite AMR Multi-Spouse Accept as true with Fund supply toughen for techniques that support world collaborative surveillance, advertise accountable antimicrobial use and pressure the advance of sustainable choices. Making sure researchers around the globe practice not unusual analysis requirements will permit extra labs ‚Äď particularly the ones in low- and middle-income nations ‚Äď to give a contribution to world surveillance efforts.
The well being of long run generations relies on the arena’s skill to make sure meals protection and give protection to public well being on a world scale. Within the ongoing combat between microbial evolution and human innovation, vigilance and suppleness are key to staying forward.













