Powering spacecraft with solar power would possibly not appear to be a problem, given how intense the Solar’s gentle can really feel on Earth. Spacecraft close to the Earth use massive sun panels to harness the Solar for the electrical energy had to run their communications programs and science tools.
Then again, the farther into area you cross, the weaker the Solar’s gentle turns into and the fewer helpful it’s for powering programs with sun panels. Even within the inside sun device, spacecraft akin to lunar or Mars rovers want selection energy resources.
As an astrophysicist and professor of physics, I train a senior-level aerospace engineering direction at the area surroundings. Probably the most key courses I emphasize to my scholars is solely how unforgiving area will also be. On this excessive surroundings the place spacecraft will have to resist intense sun flares, radiation and temperature swings from masses of levels underneath 0 to masses of levels above 0, engineers have evolved leading edge answers to energy probably the most maximum far off and remoted area missions.
So how do engineers energy missions within the outer reaches of our sun device and past? The answer is generation evolved within the Nineteen Sixties according to medical rules came upon two centuries in the past: radioisotope thermoelectric turbines, or RTGs.
RTGs are necessarily nuclear-powered batteries. However not like the AAA batteries on your TV far off, RTGs can give energy for many years whilst masses of thousands and thousands to billions of miles from Earth.
Nuclear energy
Radioisotope thermoelectric turbines don’t depend on chemical reactions just like the batteries on your telephone. As an alternative, they depend at the radioactive decay of parts to provide warmth and in the end electrical energy. Whilst this idea sounds very similar to that of a nuclear energy plant, RTGs paintings on a distinct idea.
Maximum RTGs are constructed the use of plutonium-238 as their supply of power, which isn’t usable for nuclear energy crops because it does now not maintain fission reactions. As an alternative, plutonium-238 is an risky component that may go through radioactive decay.
Radioactive decay, or nuclear decay, occurs when an risky atomic nucleus spontaneously and randomly emits debris and effort to succeed in a extra solid configuration. This procedure continuously reasons the component to turn out to be every other component, because the nucleus can lose protons.
Plutonium-238 decays into uranium-234 and emits an alpha particle, made of 2 protons and two neutrons.
NASA
When plutonium-238 decays, it emits alpha debris, which consist of 2 protons and two neutrons. When the plutonium-238, which begins with 94 protons, releases an alpha particle, it loses two protons and becomes uranium-234, which has 92 protons.
Those alpha debris have interaction with and switch power into the fabric surrounding the plutonium, which heats up that subject matter. The radioactive decay of plutonium-238 releases sufficient power that it might probably glow crimson from its personal warmth, and it’s this robust warmth that’s the power supply to energy an RTG.
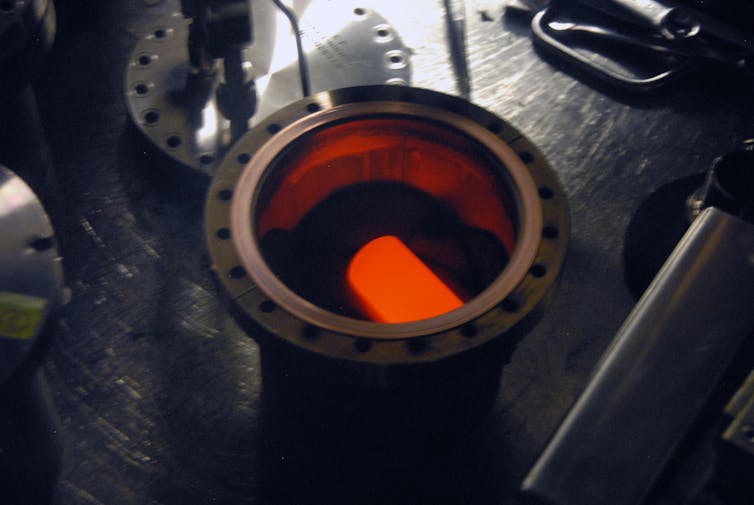

The nuclear warmth supply for the Mars Interest rover is encased in a graphite shell. The gas glows crimson scorching as a result of the radioactive decay of plutonium-238.
Idaho Nationwide Laboratory, CC BY
Warmth as energy
Radioisotope thermoelectric turbines can flip warmth into electrical energy the use of a idea known as the Seebeck impact, came upon via German scientist Thomas Seebeck in 1821. As an added receive advantages, the warmth from some sorts of RTGs can lend a hand stay electronics and the opposite parts of a deep-space challenge heat and dealing smartly.
In its fundamental shape, the Seebeck impact describes how two wires of various accomplishing fabrics joined in a loop produce a present in that loop when uncovered to a temperature distinction.
The Seeback impact is the main in the back of RTGs.
Units that use this idea are known as thermoelectric {couples}, or thermocouples. Those thermocouples permit RTGs to provide electrical energy from the adaptation in temperature created via the warmth of plutonium-238 decay and the frigid chilly of area.
Radioisotope thermoelectric generator design
In a fundamental radioisotope thermoelectric generator, you will have a container of plutonium-238, saved within the type of plutonium-dioxide, continuously in a cast ceramic state that gives additional protection within the tournament of an twist of fate. The plutonium subject matter is surrounded via a protecting layer of foil insulation to which a big array of thermocouples is hooked up. The entire meeting is inside of a protecting aluminum casing.
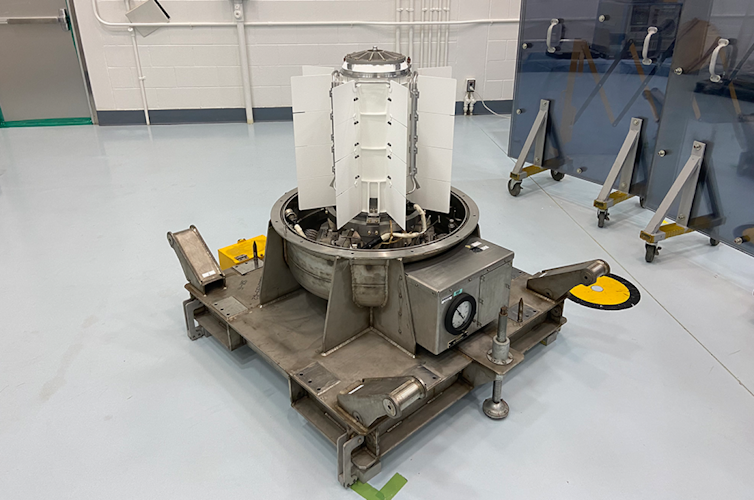

An RTG has decaying subject matter in its core, which generates warmth that it converts to electrical energy.
U.S. Division of Power
The internal of the RTG and one aspect of the thermocouples is stored scorching – as regards to 1,000 levels Fahrenheit (538 levels Celsius) – whilst the out of doors of the RTG and the opposite aspect of the thermocouples are uncovered to area. This out of doors, space-facing layer will also be as chilly as a couple of hundred levels Fahrenheit underneath 0.
This sturdy temperature distinction lets in an RTG to show the warmth from radioactive decay into electrical energy. That electrical energy powers a wide variety of spacecraft, from communications programs to science tools to rovers on Mars, together with 5 present NASA missions.
However don’t get too fascinated about purchasing an RTG for your home. With the present generation, they may be able to produce just a few hundred watts of energy. That can be sufficient to energy a regular pc, however now not sufficient to play video video games with a formidable GPU.
For deep-space missions, then again, the ones couple hundred watts are greater than sufficient.
The true advantage of RTGs is their skill to supply predictable, constant energy. The radioactive decay of plutonium is continuing – each and every 2nd of on a daily basis for many years. Over the process about 90 years, handiest part the plutonium in an RTG can have decayed away. An RTG calls for no transferring portions to generate electrical energy, which makes them a lot much less prone to ruin down or prevent running.
Moreover, they have got a very good protection document, they usually’re designed to live on their customary use and likewise be protected within the tournament of an twist of fate.
RTGs in motion
RTGs had been key to the good fortune of lots of NASA’s sun device and deep-space missions. The Mars Interest and Perseverance rovers and the New Horizons spacecraft that visited Pluto in 2015 have all used RTGs. New Horizons is touring out of the sun device, the place its RTGs will supply energy the place sun panels may just now not.
Then again, no missions seize the ability of RTGs fairly just like the Voyager missions. NASA introduced the dual spacecraft Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 in 1977 to take a excursion of the outer sun device after which adventure past it.
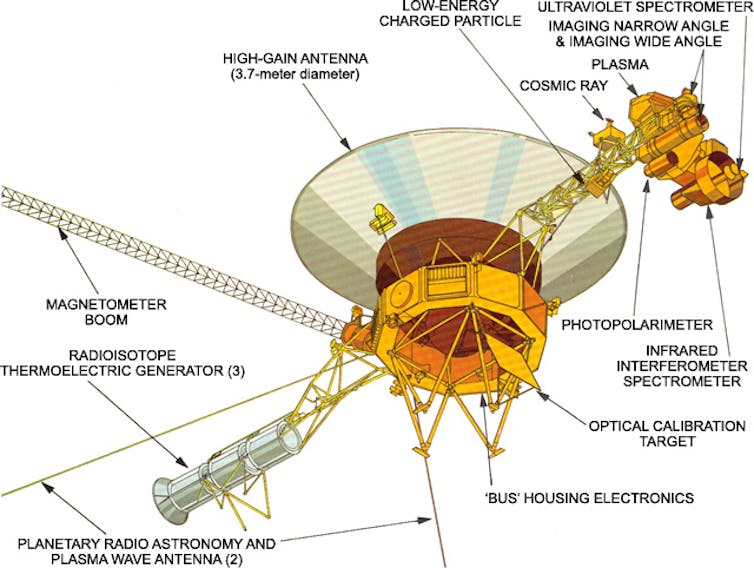
The RTGs at the Voyager probes have allowed the spacecraft to stick powered up whilst they acquire information.
NASA/JPL-Caltech
Each and every craft used to be provided with 3 RTGs, offering a complete of 470 watts of energy at release. It’s been virtually 50 years because the release of the Voyager probes, and each are nonetheless lively science missions, accumulating and sending information again to Earth.
Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 are about 15.5 billion miles and 13 billion miles (just about 25 billion kilometers and 21 billion kilometers) from the Earth, respectively, making them probably the most far away human-made gadgets ever. Even at those excessive distances, their RTGs are nonetheless offering them constant energy.
Those spacecraft are a testomony to the ingenuity of the engineers who first designed RTGs within the early Nineteen Sixties.












