The colours of rubies and emeralds are so placing that they outline sunglasses of pink and inexperienced ‚Äď ruby pink and emerald inexperienced. However have you ever ever questioned how they get the ones colours?
I‚Äôm an inorganic chemist. Researchers in my box paintings to grasp the chemistry of the entire components that make up the periodic desk. Many inorganic chemists focal point at the transition metals ‚Äď the weather in the midst of the periodic desk. The transition metals come with many of the metals you‚Äôre aware of, like iron (Fe) and gold (Au).
One characteristic of compounds made with transition metals is their intense colour. There are lots of examples in nature, together with gems and paint pigments. Even the colour of blood comes from the protein hemoglobin, which accommodates iron.
Investigating the colours of compounds containing transition metals leads you into some actually wonderful science ‚Äď that‚Äôs a part of what drew me to check this box.
Rubies and emeralds are nice examples of ways a small quantity of a transition steel ‚Äď on this case, chromium ‚Äď can create a phenomenal colour in what would another way be a somewhat boring-looking mineral.
Minerals and crystals
Rubies seem pink as a result of they soak up blue and inexperienced gentle.
benedek/E+ by means of Getty Photographs
Each rubies and emeralds are minerals, which is a kind of rock with a constant chemical composition and a extremely ordered construction on the atomic stage.
When this extremely ordered construction extends in all 3 dimensions, the mineral turns into a crystal.
With a idea advanced via physicists within the Nineteen Twenties known as crystal box idea, scientists can give an explanation for why rubies and emeralds have the colours they do. Crystal box idea makes predictions about how a transition steel ion’s construction is suffering from the opposite atoms surrounding it.
Rubies are principally made up of the mineral corundum, which consists of the weather aluminum and oxygen in a normal, repeating array. Every aluminum ion is surrounded via six oxygen ions.
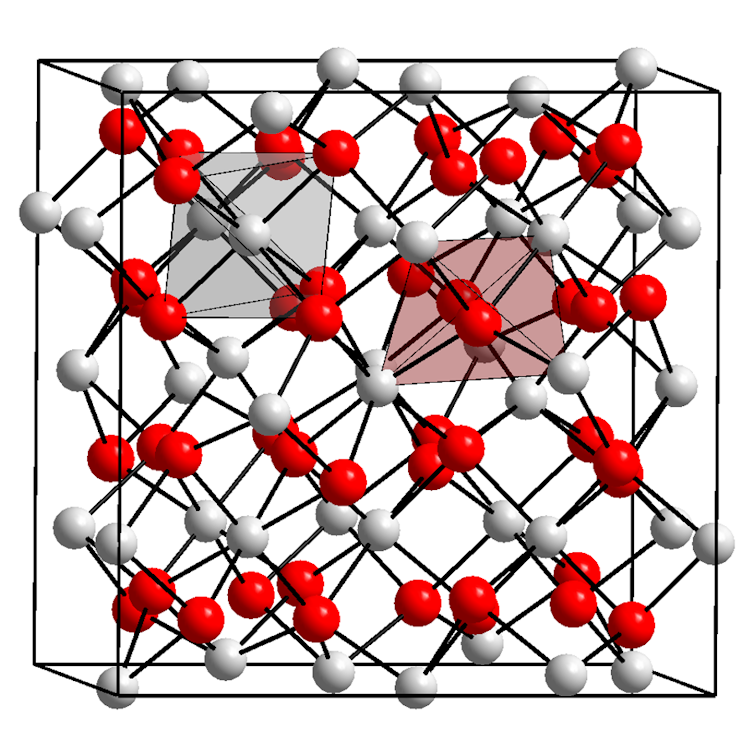
A crystal of corundum looks as if this on the atomic stage, with the aluminum ions proven as pink balls and the oxygen ions proven as white balls. Every aluminum ion is surrounded via six oxygen ions, and every oxygen via 4 aluminums.
Eigenes Werk/Wikimedia Commons, CC BY-SA
Emeralds are principally made up of the mineral beryl, which is constructed from the weather beryllium, aluminum, silicon and oxygen. Beryl’s crystal construction is extra sophisticated than corundum’s on account of the extra components within the system, however every aluminum ion is once more surrounded via six oxygen ions.

Emeralds seem inexperienced as a result of they soak up pink and blue gentle.
SunChan/E+ by means of Getty Photographs
Natural corundum and beryl are colorless. The intense colours of rubies and emeralds come from the presence of very small quantities of chromium. The chromium replaces about 1% of the aluminum within the corundum or beryl crystal when a ruby or emerald paperwork underground at a prime temperature and power.
However how can one part ‚Äď chromium ‚Äď create the pink colour of a ruby and inexperienced colour of an emerald?
Colour science
Rubies and emeralds have the colours they do as a result of, like many components, they soak up some colours of sunshine. Maximum visual gentle, like daylight, consists of the entire colours of the rainbow: pink, orange, yellow, inexperienced, blue, indigo and violet. Those colours make up the visual gentle spectrum, which is straightforward to bear in mind as ROY G BIV.
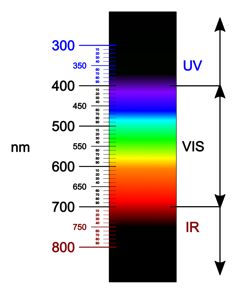
Items soak up some visual gentle wavelengths and mirror others, which is why we see them as having a colour.
Fulvio314/Wikimedia Commons, CC BY-SA
One of the crucial primary explanation why gadgets have a colour is as a result of they soak up a number of of those visual colours of sunshine. If a substance absorbs, as an example, pink gentle, it signifies that the pink gentle will get trapped within the substance and the opposite colours mirror again on your eyes. The colour you notice is the sum of the rest gentle, which might be within the green-to-blue vary. If a substance absorbs blue, it’s going to glance pink or orange to you.
Not like the colorless aluminum ion, the chromium ion absorbs blue and inexperienced gentle when surrounded via the oxygen ions. The pink gentle is mirrored again, in order that’s what you notice in rubies.
In an emerald, even if the chromium is surrounded via six oxygen ions, there’s a weaker interplay between the chromium and the encompassing oxygen ions. That’s because of the presence of silicon and beryllium within the beryl crystal. They motive the emerald to soak up blue and pink gentle, leaving the golf green so that you can see.
The power to music the homes of transition metals like chromium via converting what’s surrounding this can be a core technique in my box of inorganic chemistry. Doing so can lend a hand scientists perceive the elemental science of metal-containing compounds and the design of chemical substances for particular functions.
You’ll take satisfaction within the wonderful colours of the gems, however via chemistry, you’ll be able to additionally see how nature creates the ones colours the usage of an unending number of complicated constructions made with the weather within the periodic desk.













