ValentineŌĆÖs Day continuously conjures pictures of sweets and romance. However the crop at the back of this indulgence faces an existential risk.
Areas like northeastern Brazil, one of the crucial internationalŌĆÖs notable cocoa-producing spaces, are grappling with expanding aridity ŌĆō a sluggish, but unrelenting drying of the land. Cocoa is made out of the beans of the cacao tree, which flourishes in humid climates. The crop is suffering in those drying areas, and so are the farmers who develop it.
This isnŌĆÖt simply BrazilŌĆÖs tale. Throughout West Africa, the place 70% of the sectorŌĆÖs cacao is grown, and within the Americas and Southeast Asia, transferring moisture ranges threaten the sophisticated steadiness required for manufacturing. Those areas, house to colourful ecosystems and world breadbaskets that feed the sector, are at the frontlines of aridityŌĆÖs sluggish however relentless advance.
A farmer in Colombia holds a cacao pod, which holds the important thing substances for chocolate.
┬®2017CIAT/NeilPalmer, CC BY-NC-SA
Over the last 30 years, greater than three-quarters of the EarthŌĆÖs landmass has turn into drier. A up to date record I helped coordinate for the United Countries Conference to Struggle Desertification discovered that drylands now duvet 41% of world land, a space that expanded via just about 1.7 million sq. miles (4.3 million sq. kilometers) over the ones 3 many years ŌĆö about part the dimensions of Australia.
This creeping dryness is not only a local weather phenomenon. ItŌĆÖs a long-term transformation that can be irreversible and that carries devastating penalties for ecosystems, agriculture and livelihoods international.
What reasons aridity?
Aridity, whilst continuously regarded as purely a local weather phenomenon, is the results of a posh interaction amongst human-driven components. Those come with greenhouse gasoline emissions, land use practices and the degradation of vital herbal assets, reminiscent of soil and biodiversity.
Those interconnected forces were accelerating the transformation of once-productive landscapes into increasingly more arid areas, with penalties that ripple throughout ecosystems and economies.
Greenhouse gasoline emissions: A world catalyst
Human-induced local weather trade is the principle driving force of emerging aridity.
Greenhouse gasoline emissions, specifically from fossil gas combustion and deforestation, build up world temperatures. Emerging temperatures, in flip, motive moisture to evaporate at a quicker charge. This heightened evaporation reduces soil and plant moisture, exacerbating water shortage ŌĆō even in areas with average rainfall.
Aridity started accelerating globally within the Fifties, and the sector has observed a pronounced shift during the last 3 many years.
This procedure is especially stark in areas already susceptible to dryness, reminiscent of AfricaŌĆÖs Sahel area and the Mediterranean. In those spaces, decreased precipitation ŌĆō mixed with greater evaporation ŌĆō creates a comments loop: Drier soils soak up much less warmth, leaving the ambience hotter and intensifying arid prerequisites.
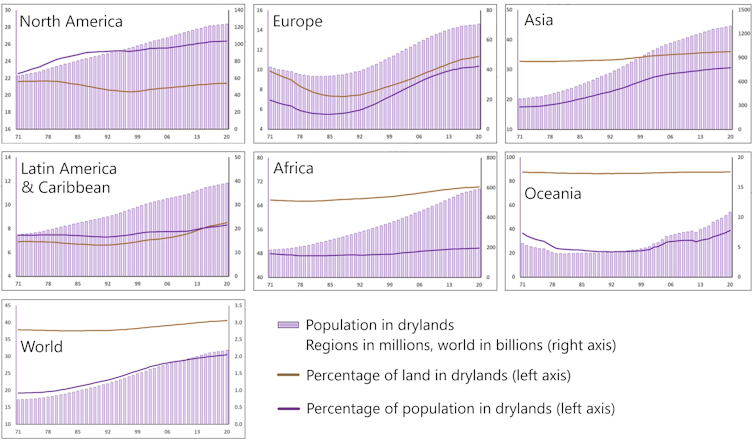
The choice of other folks dwelling in dryland areas has been emerging in each and every area lately. Years 1971-2020. Scales range.
UNCCD
Unsustainable land use practices: A hidden accelerator
Aridity could also be suffering from how other folks use and set up land.
Unsustainable agricultural practices, overgrazing and deforestation strip soils in their protecting plants duvet, leaving them liable to erosion. Business farming ways continuously prioritize non permanent yields over long-term sustainability, depleting vitamins and natural topic very important for wholesome soils.
As an example, in cocoa-producing areas like northeastern Brazil, deforestation to make room for agriculture disrupts native water cycles and exposes soils to degradation. With out plants to anchor it, topsoil ŌĆō vital for plant enlargement ŌĆō washes away all the way through rainfall or is blown away via winds, taking with it necessary vitamins.
Those adjustments create a vicious cycle: Degraded soils additionally grasp much less water and result in extra runoff, decreasing the landŌĆÖs talent to recuperate.

Aridity can have an effect on the facility to develop many vegetation. Massive portions of the rustic of Chad, proven right here, have drying lands.
United Countries Chad, CC BY-NC-SA
The soil-biodiversity connection
Soil, continuously lost sight of in discussions of local weather resilience, performs a vital function in mitigating aridity.
Wholesome soils act as reservoirs, storing water and vitamins that vegetation rely on. In addition they toughen biodiversity beneath and above floor. A unmarried teaspoon of soil comprises billions of microorganisms that lend a hand cycle vitamins and take care of ecological steadiness.
Then again, as soils degrade underneath aridity and mismanagement, this biodiversity diminishes. Microbial communities, very important for nutrient biking and plant well being, decline. When soils turn into compacted and lose natural topic, the landŌĆÖs talent to retain water diminishes, making it much more vulnerable to drying out.
Briefly, the lack of soil well being creates cascading results that undermine ecosystems, agricultural productiveness and meals safety.
International sizzling spots: Looming meals safety crises
Cocoa is only one crop suffering from the encroachment of emerging aridity.
Different key agricultural zones, together with the breadbaskets of the sector, also are in danger. Within the Mediterranean, AfricaŌĆÖs Sahel and portions of the U.S. West, aridity already undermines farming and biodiversity.
Via 2100, as much as 5 billion other folks may just reside in drylands ŌĆō just about double the present inhabitants in those spaces, because of each inhabitants enlargement and growth of drylands because the planet warms. This places immense power on meals programs. It will probably additionally boost up migration as declining agricultural productiveness, water shortage and irritating dwelling prerequisites drive rural populations to transport looking for alternatives.
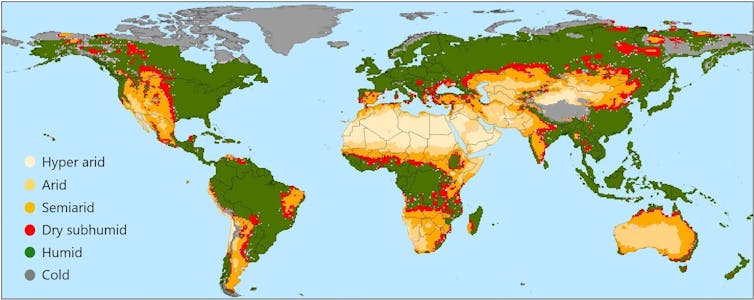
A map displays reasonable aridity for 1981-2010. Laptop simulations estimate that greenhouse gasoline emissions from human actions brought about a 1.2% higher build up within the 4 kinds of dry areas mixed for the sessions between 1850 and 1981ŌĆō2010 than simulations with simplest sun and volcanic results thought to be.
UNCCD
AridityŌĆÖs ripple results additionally prolong a ways past agriculture. Ecosystems, already strained via deforestation and air pollution, are wired as water assets dwindle. Natural world migrates or dies, and plant species tailored to moister prerequisites canŌĆÖt live on. The SahelŌĆÖs subtle grasslands, as an example, are swiftly giving method to wilderness shrubs.
On a world scale, financial losses related to aridification are staggering. In Africa, emerging aridity contributed to a 12% drop in gross home product from 1990 to 2015. Sandstorms and mud storms, wildfires and water shortage additional burden governments, exacerbating poverty and well being crises in probably the most affected areas.
The trail ahead
Aridity isnŌĆÖt inevitable, nor are its results utterly irreversible. However coordinated world efforts are very important to curb its development.
International locations can paintings in combination to revive degraded lands via protective and restoring ecosystems, making improvements to soil well being and inspiring sustainable farming strategies.
Communities can set up water extra successfully thru rainwater harvesting and complex irrigation programs that optimize water use. Governments can cut back the drivers of local weather trade via making an investment in renewable power.
Endured world collaboration, together with running with companies, can lend a hand proportion applied sciences to make those movements simpler and to be had international.
So, as you savor chocolate this ValentineŌĆÖs Day, take into account the delicate ecosystems at the back of it. The cost of cocoa in early 2025 was once close to its all-time prime, due partly to dry prerequisites in Africa. With out pressing motion to deal with aridity, this situation might turn into extra not unusual, and cocoa ŌĆō and the candy concoctions derived from it ŌĆō might smartly turn into an extraordinary luxurious.
Collective motion in opposition to aridity isnŌĆÖt as regards to saving chocolate ŌĆō itŌĆÖs about holding the planetŌĆÖs capability to maintain lifestyles.













